Berberine and PCOS: Benefits, Risks, Dosage, and Whether It’s Right for You
The complete dietitian-approved guide to understanding how berberine supports insulin resistance, hormone balance, and metabolic health.
PCOS and Berberine: Everything You Need to Know
Berberine has become one of the most talked-about supplements for PCOS, particularly for women struggling with insulin resistance, high androgens, inflammation, and difficulty losing weight. It’s often compared to metformin—and early research suggests it may be just as effective (and in some cases, better tolerated).
But like every supplement in the PCOS world, berberine isn’t for everyone. And without the right nutrition and lifestyle foundations in place, it won't deliver the results you're hoping for.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn:
What berberine is and how it works
Why berberine is helpful for PCOS (insulin, inflammation, ovulation, lipids)
How it compares to metformin
Potential side effects & who shouldn’t take it
Research-backed dosages & timing
How berberine fits into a holistic PCOS plan
Dietitian-approved alternatives if berberine isn’t right for you
Let’s dive in.
What Is Berberine?
Berberine is a bioactive compound naturally found in plants like:
Goldenseal
Barberry
Oregon grape
Tree turmeric
It has been used in traditional Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine for centuries.
Modern research highlights berberine as a powerful tool for:
Lowering blood sugar
Improving insulin sensitivity
Reducing inflammation
Supporting gut health
Balancing cholesterol
Assisting moderate weight loss
These mechanisms make it particularly relevant for people with PCOS, where insulin resistance is one of the biggest drivers of symptoms.
Why Women With PCOS Are Turning to Berberine
1. Berberine Supports Insulin Resistance (One of the Root Causes of PCOS)
Up to 80% of women with PCOS struggle with insulin resistance—even those who aren’t overweight.
Berberine helps your body:
Respond better to insulin
Move glucose into your cells (instead of storing it as fat)
Reduce fasting insulin
Lower A1C and blood glucose
This is why many women notice improvements in:
Energy
Cravings
Belly fat
Fertility
Irregular periods
When insulin improves, hormones begin to rebalance.
2. Berberine Helps Lower Testosterone and Reduce Androgen Symptoms
High androgens can cause:
Acne
Facial hair growth
Scalp hair loss
Irregular cycles
Anovulation
By improving insulin sensitivity, berberine indirectly reduces excess testosterone production, helping support:
Clearer skin
More regular cycles
Less hair growth on the chin/jawline
Healthier scalp hair retention
3. Berberine May Support Weight Loss (Especially Belly Fat)
Research shows berberine may help with modest weight reduction, especially central adiposity, due to its effects on:
Insulin
Fat metabolism
Gut microbiome
Inflammation
Important note: Berberine is not a weight-loss pill. It works best when paired with nutrition foundations: balanced meals, consistent protein, fiber, strength training, and good sleep.
4. Berberine Supports Cholesterol and Heart Health
Women with PCOS are at significantly higher risk of:
High LDL
High triglycerides
Low HDL
Fatty liver
Cardiometabolic disease
Berberine may help lower:
LDL
Triglycerides
Total cholesterol
This is especially helpful for women who cannot tolerate statins or have early signs of metabolic syndrome.
5. Berberine Supports Ovulation and Fertility
Several clinical trials have shown berberine may:
Improve ovulation frequency
Support regular cycles
Improve egg quality markers
Support women with PCOS undergoing IVF
Improve insulin-related anovulation
Many women report more predictable cycles and improved fertility within 8–12 weeks of consistent use (paired with nutrition support).
What the Research Says About Berberine for PCOS
Research over the past decade has shown that berberine can improve multiple aspects of PCOS—including metabolic, hormonal, and reproductive outcomes.
Reproductive Improvements
Some studies have found that berberine + lifestyle changes prior to assisted reproductive technology (ART) were associated with higher live birth rates than lifestyle changes alone. However, when berberine was combined with letrozole, no significant effect on live birth rate was observed.
Metabolic Improvements
Berberine has demonstrated:
Better lipid profiles (lower LDL & triglycerides)
Improvements in insulin sensitivity
Potential benefits for fatty liver disease
Interestingly, the strongest lipid-lowering effects were shown in non-PCOS studies lasting 6 months, while most PCOS-specific trials lasted only 3 months—suggesting benefits may continue with longer use.
Comparison to Other PCOS Treatments
Berberine has shown comparable effects to both metformin and myo-inositol for improving:
Insulin resistance
Hormone imbalance
Metabolic markers
However, berberine often performs best when combined with other treatments, particularly metformin or lifestyle interventions, rather than as a standalone treatment.
Typical Research Dosage
Most studies use:
500–600 mg, taken 2–3x daily (1,000–1,500 mg total).
This aligns with the practical dosage recommended later in this guide.
How to Take Berberine for PCOS: Dosage, Timing, and Best Practices
The most research-backed dose:
1,000–1,500 mg per day, divided into 2–3 doses.
Why divided? Berberine has a short half-life, so spreading it out improves effectiveness.
Best timing:
500 mg with breakfast
500 mg with lunch
Optional 500 mg with dinner if insulin resistance or cravings are significant
Do not take berberine on an empty stomach.
How Long Does Berberine Take to Work for PCOS?
Most women notice:
Better energy → 1–2 weeks
Reduced cravings → 1–3 weeks
More stable blood sugar → 2–4 weeks
Cycle improvements → 2–3 months
Visible androgen symptom support → 3–6 months
Lipid improvements → 8–12 weeks
Consistency matters more than perfection.
Berberine Side Effects & Who Should Avoid It
Common Side Effects
Nausea
Gas
Constipation or diarrhea
Appetite reduction
Headache
Yellowing of stool
Side effects often improve after 1–2 weeks.
Who Should NOT Take Berberine
Do NOT use berberine if you:
Are pregnant or trying to conceive naturally soon
Are breastfeeding
Take diabetes or blood pressure medications without supervision
Have low blood sugar
Take cyclosporine or anticoagulants
Have liver or kidney disease
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting.
PCOS Diet + Berberine: Why What You Eat Matters More Than the Supplement
Berberine will not work well if:
You are under-eating
You skip meals
You eat carbs alone
You’re inflamed
You’re sleeping poorly
You’re chronically stressed
To maximize benefits, pair berberine with:
Foundational PCOS Nutrition
Eat protein first
Include 20–30g protein per meal
Pair carbs with fiber + fat + protein
Reduce ultra-processed snacking
Prioritize anti-inflammatory foods
Add soluble fiber daily
Best Foods for Insulin Resistance
Avocado
Olive oil
Nuts & seeds
Chia, flax, psyllium
Beans & lentils
Greens
Berries
Eggs
Salmon
Berberine amplifies progress only when the foundation is in place.
Berberine Alternatives for PCOS
Evidence-supported alternatives include:
Inositol (myo + DCI 40:1)
Cinnamon extract
Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA)
Chromium
Omega-3s
NAC
Metformin
Some women benefit from combining inositol + berberine, but this requires practitioner supervision.
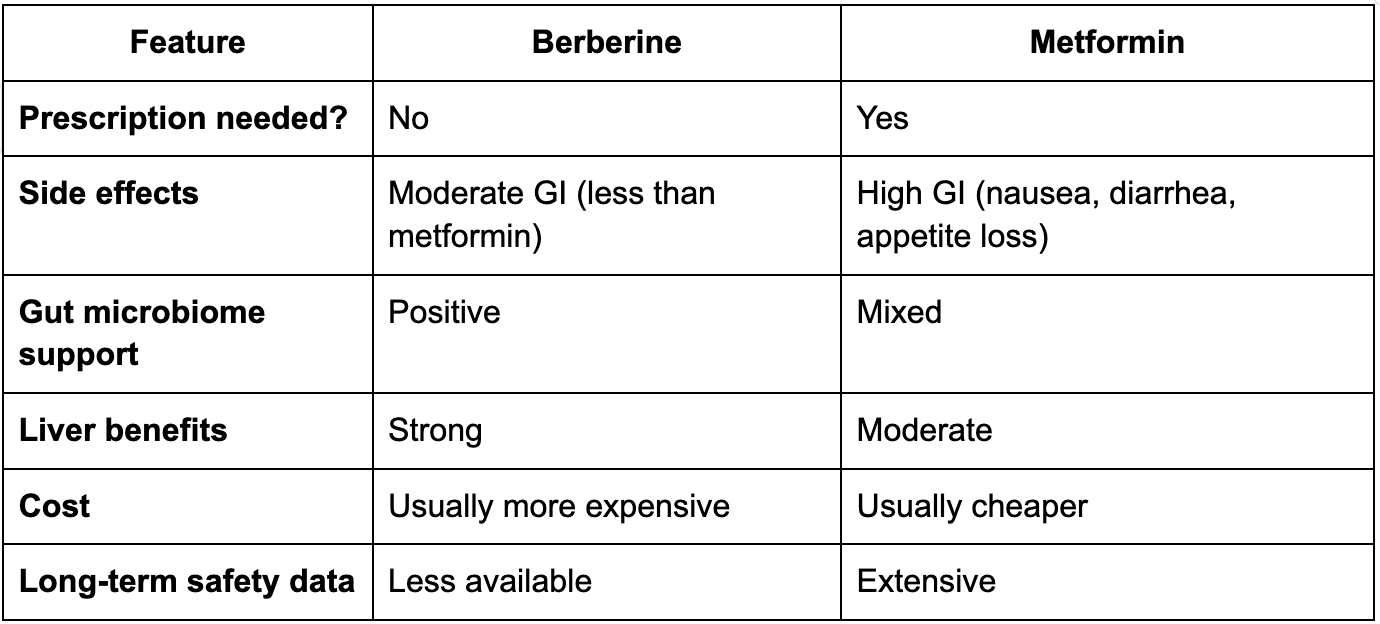
Berberine vs. Metformin for PCOS: Which Is Better?
Both can:
Improve insulin sensitivity
Lower blood sugar
Support ovulation
Reduce androgens
Support modest weight loss
Differences:
Many women try berberine due to metformin intolerance or desire for a holistic option.
Is It Safe to Take Berberine With Metformin?
Short answer: Sometimes, but only with medical supervision.
Both work through similar pathways (insulin, glucose output, AMPK activation), so combining them can:
Improve blood sugar
Improve lipids
Support ovulation
But may also:
Increase low blood sugar risk
Worsen GI distress
Reduce appetite excessively
See the original section for dosing strategy, risks, and practitioner perspective (kept intact).
Is Berberine Right for You? A Dietitian’s Perspective
Berberine can be powerful for:
✔ Insulin resistance
✔ Blood sugar crashes
✔ Belly fat
✔ High testosterone
✔ High cholesterol
✔ Metformin intolerance
But it is not a standalone solution.
PCOS requires a root-cause, holistic approach.
Final Takeaway: Berberine Works Best With the Right Foundations
When paired with:
Balanced meals
Protein
Fiber
Stress support
Movement
Blood sugar stability
Berberine becomes far more effective.
If you want a personalized PCOS plan tailored to your hormones, metabolism, and long-term goals, I’d love to support you.
✨ Work with me 1:1 for customized nutrition and supplement guidance.