PCOS and GLP-1s: Is It Right for You? Everything You Need to Know Before Starting
GLP-1 medications like Ozempic®, Wegovy®, and Mounjaro® have exploded in popularity—and many women with PCOS are wondering whether these drugs might finally help them lose weight, improve insulin resistance, reduce cravings, and get their hormones back on track.
The truth? GLP-1s can be incredibly effective for some women with PCOS—but they are not the first step, not the only option, and not the right choice for everyone. They also come with important warnings, fertility considerations, and side effects that women aren’t always told about upfront.
This comprehensive guide breaks down how GLP-1s work, who they help most, what to expect, what to try before medication, side effects, alternatives, and essential safety information for women with PCOS.
What Are GLP-1 Medications?
GLP-1 receptor agonists (such as liraglutide, semaglutide, and tirzepatide) were originally created for type 2 diabetes. Research now shows they may be helpful for PCOS because they mimic glucagon-like peptide-1, a hormone involved in:
Appetite regulation
Insulin secretion
Blood sugar stability
Gastric emptying
Satiety and fullness
For women with PCOS—especially those with stubborn weight gain and insulin resistance—these mechanisms can be profoundly helpful.
Research has demonstrated that GLP-1 receptor agonists may lead to significant weight loss, improved metabolic markers, improved body composition, and even improvements in some hormonal parameters in PCOS. They are now recommended adjuncts to lifestyle interventions for higher-weight adults with PCOS following general obesity treatment guidelines.
How GLP-1s Work for PCOS
Research shows GLP-1 medications may support PCOS management by:
✔ Reducing Insulin Resistance
One of the biggest drivers of:
Weight gain around the midsection
Cravings
Irregular cycles
Androgen excess
GLP-1s help stabilize blood sugar and improve the body’s response to insulin.
✔ Lowering Appetite + Cravings
Blood sugar crashes are common in PCOS and can cause intense carb cravings. GLP-1s slow digestion, increase fullness, and help prevent post-meal crashes.
✔ Supporting Weight Loss
Many women lose 10–20% of their body weight on GLP-1s—though not guaranteed. Weight loss tends to be greater when:
Insulin resistance is present
Emotional eating decreases
Nutrition habits shift alongside medication
✔ Improving Metabolic & Fertility Markers
Some studies show improvements in:
Cycle regularity
Ovulation frequency
Insulin resistance
Body composition
Inflammation
Not because GLP-1s “fix” hormones, but because they reduce metabolic stress that disrupts ovulation.
What the Research Says (In Plain English)
GLP-1s work best when combined with nutrition and lifestyle, not used alone.
They can improve weight, insulin resistance, lipid levels, inflammation, and sometimes androgen levels.
They may not improve all PCOS symptoms—especially hirsutism or hair loss—which often require additional interventions.
Weight regain after stopping GLP-1s is common, which is why long-term planning matters.
GLP-1s require effective contraception because pregnancy safety data is lacking.
Providers recommend slow dose escalation to reduce GI side effects.
A Dietitian’s Perspective: The Side of GLP-1s No One Talks About Enough
As a dietitian who works closely with women with PCOS, I’m seeing a pattern that isn’t being talked about enough. While GLP-1 medications can be transformative for the right person, many women are showing up in my practice struggling with side effects that go far beyond “a little nausea.”
The most common issues I see include:
Near-total loss of appetite
Persistent nausea or bloating
Daily GI discomfort or constipation lasting days
Inability to tolerate balanced meals
Protein intake dropping dramatically
Visible muscle loss on body composition scans
Severe fatigue because they’re barely eating
Here’s the problem:
GLP-1s are meant to reduce appetite—not eliminate your ability to eat enough to sustain metabolic, hormonal, and emotional health.
For women with PCOS, the foundation of healing requires:
Stable blood sugar
Consistent protein intake
Fiber for gut health + estrogen metabolism
Micronutrients that support ovulation
Enough calories to prevent metabolic slowdown
When someone can’t even finish half a meal without nausea or discomfort, that’s not “normal,” and it’s not therapeutic—it’s a red flag.
Why This Hits Women With PCOS Even Harder
Women with PCOS are already more vulnerable to:
Metabolic inflexibility
Nutrient deficiencies (iron, vitamin D, magnesium, omega-3s)
Gut issues
Appetite dysregulation
Hormonal imbalances
So when GLP-1 side effects push food intake too low, it can actually worsen:
Blood sugar crashes
Cortisol and stress hormone output
Cycle irregularity
Hair loss
Anxiety
Low energy
Slower metabolism
Loss of lean muscle (which raises insulin resistance long-term)
Many women tell me:
“I’m losing weight, but I feel awful.”
“I’m barely eating anything.”
“My stomach hurts constantly.”
Weight loss should never come at the expense of foundational health.
What I Wish More Providers Told Women Before Starting GLP-1s
✔ You may need a nutrition plan before the first dose — especially for protein, electrolytes, and meal structure.
✔ Rapid weight loss is often rapid muscle loss unless you actively prevent it through protein + resistance training.
✔ GI symptoms aren’t “normal” just because they’re common.
Persistent nausea or inability to eat enough requires adjustment.
✔ GLP-1s require more lifestyle support—not less.
They don’t replace nutrition; they amplify the need for it.
✔ Without habits in place, weight regain after stopping is likely.
This is why pairing medication with nutrition support matters.
If You’re on a GLP-1 and Feeling Unwell, You’re Not Alone
You may need:
A slower titration schedule
A dose change
A protein + electrolyte strategy
GI-soothing nutrition support
Strength training adjustments
Supplementation to protect metabolism
A deeper look at your PCOS root cause
You do not need to suffer through symptoms or blame yourself for “not tolerating it well.”
My Role Isn’t to Convince You For or Against GLP-1s—It’s to Protect Your Health While You’re On Them (or Before You Start)
If you choose to use a GLP-1, you deserve guidance that protects your:
Hormones
Muscle mass
Gut health
Metabolism
Energy
Mental clarity
Most of the issues I see are preventable with the right plan in place.
Is a GLP-1 Medication Right for You?
GLP-1s may be appropriate if you have:
1. Moderate to Severe Insulin Resistance
Signs include:
Intense carb/sugar cravings
Acanthosis nigricans
Energy crashes
Difficulty losing weight
2. BMI ≥ 27–30 + Metabolic Symptoms
Such as:
Prediabetes
High triglycerides
High fasting insulin
Fatty liver
3. Long-Term Difficulty Losing Weight Despite Effort
4. Appetite Dysregulation or Binge Cravings Linked to Blood Sugar
5. Preparing for Fertility Treatment
Some providers use GLP-1s pre-IVF to improve metabolic outcomes.
Who Should Not Use GLP-1s
GLP-1s are generally not recommended for:
Pregnancy or breastfeeding
Trying to conceive soon
Personal or family history of medullary thyroid cancer
Severe GI conditions (gastroparesis, pancreatitis, severe GERD)
Underweight BMI or very low appetite
Active eating disorders
Women whose PCOS is lean type or primarily adrenal/stress-driven
What to Try Before Starting a GLP-1
Nearly all guidelines recommend addressing these foundations first:
1. Blood-Sugar-Balancing Nutrition
25–35 g protein per meal
Fiber-rich meals
Pair carbs with protein + fat
Regular meals (avoid extreme fasting)
Front-loaded calories earlier in the day
2. Strength Training
Improves insulin sensitivity for up to 48 hours.
3. Sleep Optimization
Poor sleep can worsen PCOS symptoms and insulin resistance.
4. Stress + Nervous System Support
Cortisol spikes worsen cravings, insulin resistance, and cycle irregularity.
5. Foundational Supplements
Inositol
Berberine
Omega-3s
Vitamin D
Magnesium
6. Identify Your PCOS Root Cause
Not all PCOS is insulin-driven.
Some need:
Gut healing
Adrenal support
Post-pill regulation
Thyroid care.
What Happens When You Take a GLP-1 Medication?
Here’s what most women experience in the first several months:
Month 1: Adjustment
Appetite drops
Smaller meals feel filling
Mild nausea common
Month 2–3: Early Shifts
Steady weight loss
More stable energy
Reduced bloating
Month 3–6: Metabolic Improvements
Better blood sugar
Improved insulin sensitivity
Potential cycle improvement
Beyond 6 Months
Plateaus are normal
Long-term habits determine long-term success
Potential Side Effects
Most occur during dose increases.
Common:
Nausea
Bloating
Constipation/diarrhea
Early fullness
Fatigue
Headaches
Less Common but Important:
Severe GI distress
Gallbladder issues
Pancreatitis
Significant reflux
Major Risk for PCOS: Muscle Loss
Higher risk if:
Protein intake is low
Strength training is absent
Weight loss is rapid
This is why nutrition + movement planning is non-negotiable.
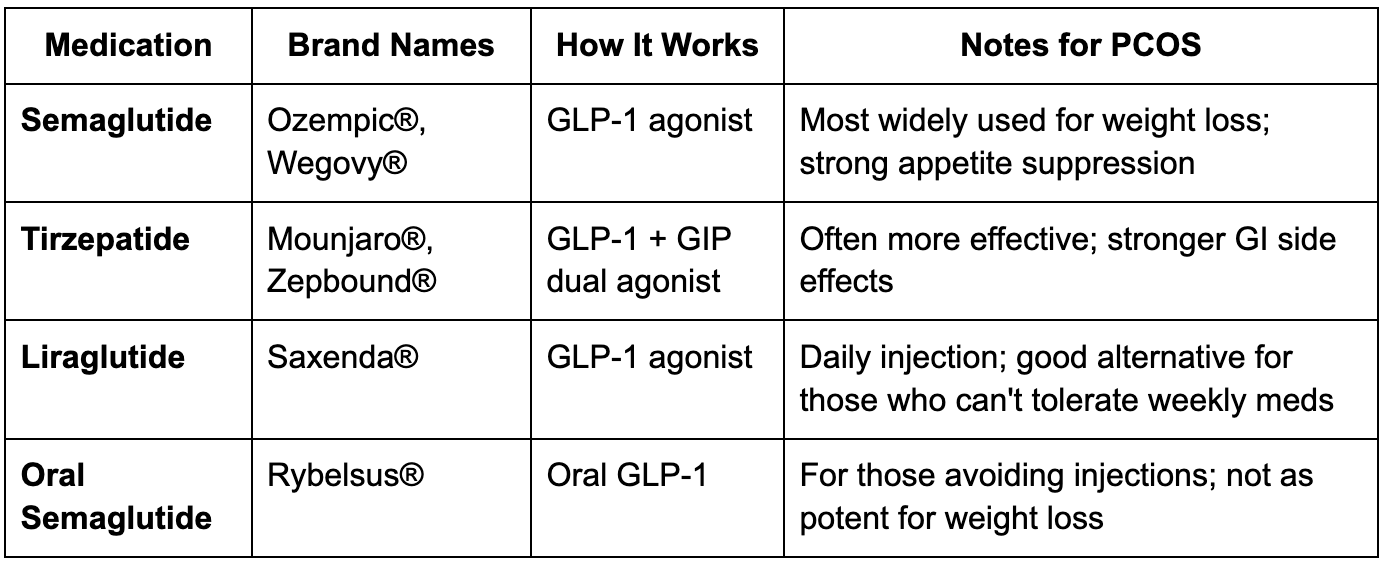
GLP-1 Options: What’s Available?
Semaglutide (Ozempic®, Wegovy®) – weekly
Tirzepatide (Mounjaro®, Zepbound®) – weekly, dual GLP-1 + GIP
Liraglutide (Saxenda®) – daily
Oral semaglutide (Rybelsus®) – daily tablet
What Happens If You Stop a GLP-1?
This is a question women aren’t warned about enough. GLP-1 medications work only while you’re taking them. Once discontinued:
✔ Appetite returns to baseline
Hunger hormones normalize, and cravings can come back stronger.
✔ Weight regain is common
Studies show many people regain most—and sometimes all—of the weight within 12–18 months if supportive habits aren’t in place.
✔ Insulin resistance may worsen again
Especially if underlying lifestyle and nutrition factors were never addressed.
✔ Emotional eating patterns can resurface
If GLP-1s were masking dysregulated appetite or stress eating, those patterns may re-emerge.
✔ GI symptoms resolve
For those who struggled with nausea and bloating, these usually improve within weeks.
This is why pairing GLP-1s with a dietitian is so essential.
The medication is a tool—not the foundation.
Your habits, nutrition strategy, and metabolic health are the foundation.
Important Safety Considerations for Women with PCOS
✔ Contraception is essential
There is insufficient safety data for GLP-1 use during pregnancy.
You must use effective birth control while on these medications.
✔ You cannot take GLP-1s while trying to conceive
Most providers recommend stopping 8–12 weeks before TTC or IVF.
✔ Slow titration matters
Increasing doses too quickly increases risk of nausea, vomiting, reflux, and gastroparesis-like symptoms.
✔ Long-term use may be necessary
For many people, GLP-1s become a chronic therapy.
This should be part of your shared decision-making.
✔ They do not treat all PCOS symptoms
Especially:
Hirsutism
Scalp hair loss
Acne
PMS
Ovulation issues not tied to insulin resistance
These often require additional treatment approaches.
Alternatives to GLP-1 Medications
If GLP-1s aren’t accessible, safe, or desirable for you, you still have evidence-based options that support metabolic health and weight management.
1. Inositol (Myo + D-Chiro)
One of the most researched supplements for PCOS.
Supports:
Ovulation
Insulin sensitivity
Androgen balance
Egg quality
Often used as first-line therapy.
2. Berberine
Shown in several studies to be as effective as metformin for insulin resistance.
Also may:
Improve gut microbiome
Reduce inflammation
Lower triglycerides
Great option for women who cannot tolerate metformin.
3. Metformin
A long-standing medication that:
Improves insulin resistance
Reduces glucose output
Supports cycle regularity
Often used alone or alongside lifestyle changes.
4. Anti-Inflammatory, Blood-Sugar-Balancing Nutrition
Foundational for every PCOS type.
Focus on:
Protein-rich meals
High-fiber carbohydrates
Healthy fats
Consistent meal timing
Limiting ultra-processed foods
5. Strength Training
One of the most powerful tools for insulin resistance.
Just 2–3 sessions/week can:
Improve glucose uptake
Increase muscle mass (your metabolic engine)
Support appetite regulation
Support long-term weight management
6. Nervous System & Stress Regulation
PCOS symptoms worsen when stress hormones are high.
Research shows cortisol dysregulation can mimic or intensify insulin resistance.
Effective tools include:
Breathwork
Slow mornings
Evening wind-down routines
Therapy or coaching
Nervous system nutrition
7. Gut Healing & Anti-Inflammatory Support
Gut imbalances can worsen:
Insulin resistance
Inflammation
Bloating
Hormonal symptoms
Targeted protocols may include:
Prebiotics
Probiotics
Digestive support
Anti-inflammatory herbs
So… Are GLP-1s the Right Choice for You?
GLP-1s may be the right choice if:
You have significant insulin resistance
You’ve tried nutrition + lifestyle changes with limited progress
Your appetite feels dysregulated or extreme
You need metabolic improvement before fertility treatment
You’re open to long-term use
You can commit to structured nutrition and movement support
Alternatives may be better if:
You prefer a non-pharmaceutical approach
You’re planning pregnancy soon
Your PCOS is lean type or stress-driven
You have strong GI sensitivity
You have a history of eating disorders
You don’t want long-term medication
A GLP-1 is a tool—not a magic fix.
When combined with metabolic nutrition, stress support, sleep optimization, and strength training, it can be life-changing.
Used alone, the results rarely last.
My Dietitian Perspective: Who Thrives on GLP-1s (and Who Doesn’t)
Women who thrive:
Those with severe insulin resistance
Those who’ve struggled with binge cravings
Those whose appetite is dysregulated, not low
Those with strong nutrition foundations
Those able to maintain protein + strength training
Women who struggle:
Those who already undereat
Those with nausea-prone stomachs
Those with “PCOS without insulin resistance”
Those not prepared with nutrition guidance
Those hoping it will fix their hormones alone
The best outcomes happen when medication is combined with functional nutrition, root-cause work, and strength training.
Your PCOS & GLP-1 Plan: How to Use These Medications Safely and Successfully
If you choose to use a GLP-1, here’s how to protect your metabolism and hormones:
✔ Eat protein first
Aim for 25–35 g per meal.
✔ Don’t skip meals
Even if appetite is low, structured eating supports metabolism.
✔ Supplement wisely
Electrolytes, magnesium, vitamin D, omega-3s.
✔ Strength train
This preserves lean muscle while losing fat.
✔ Support digestion
Warm foods, ginger, peppermint, and slowing down meals can help nausea.
✔ Monitor symptoms
Especially: persistent nausea, vomiting, constipation, dizziness, hair loss, severe fatigue.
✔ Plan your exit strategy
If you decide to stop, taper thoughtfully with support.
The Bottom Line: Are GLP-1s Right for PCOS?
GLP-1s can be powerful tools—but they are not magic.
PCOS is a multi-layered condition, and medication will not “fix” the root cause alone.
They can help you:
Reduce insulin resistance
Lose weight
Normalize cycles
Improve metabolic health
But only when paired with:
Nutrition
Strength training
Gut + inflammation support
Nervous system regulation
GLP-1s are a tool—you are the foundation.
Thinking About GLP-1s for PCOS? Let’s Create a Personalized Plan
As a Registered Dietitian, I help women understand their root-cause PCOS type, stabilize blood sugar, balance hormones, and build a sustainable metabolic foundation—with or without medication.
If you're considering a GLP-1, I can help you:
Assess whether you’re a good candidate
Build a nutrition plan that prevents muscle loss
Stabilize blood sugar naturally
Reduce side effects
Support your hormones long term
→ Click here to apply for 1:1 PCOS nutrition coaching.
You don’t have to figure this out alone.